Section 15.3 Chapter 15 Exercises
Subsection 15.3.1 Section 15.1 Homework
1. To deliver mail in a particular neighborhood, the postal carrier needs to walk along each of the streets with houses (the dots). See Graph A of Figure 15.3.1. Create a graph with edges showing where the carrier must walk to deliver the mail.
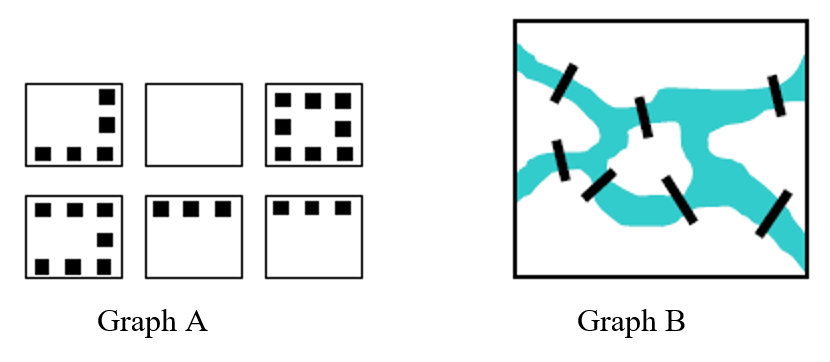
2. Suppose that a town has 7 bridges as pictured in Graph B of Figure 15.3.1. Create a graph that could be used to determine if there is a path that crosses all bridges once.
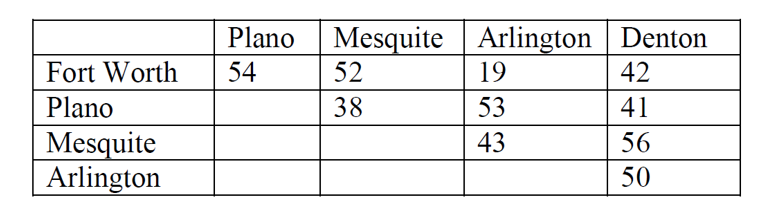
3. The table in Figure 15.3.2 below shows approximate driving times (in minutes, without traffic) between five cities in the Dallas area. Create a weighted graph representing this data.
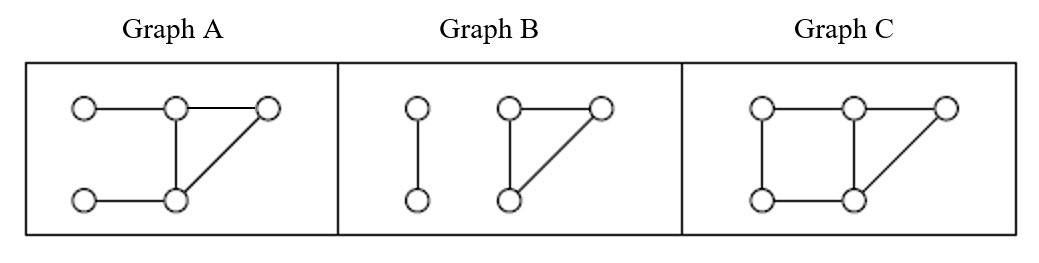
4. Identify the bridges (if any) in each of the graphs in Figure 15.3.3.
5. Draw a graph to fit each of the descriptions below. Label each vertex. Then for each graph, provide the following information: (i) next to each vertex, write its degree; (ii) give the total number of edges; (iii) give the total number of components.
- a. It has at least 7 vertices and exactly one bridge.
- b. It has at least six edges and at least two components.
- c. It has exactly four vertices each of degree 3.
- d. It is connected and has five vertices, exactly one of which has degree 1. Does your graph have any bridges?
- e. It is connected and has five vertices, all of which have degree 2. Does this graph have any bridges?
Subsection 15.3.2 Section 15.2 Homework
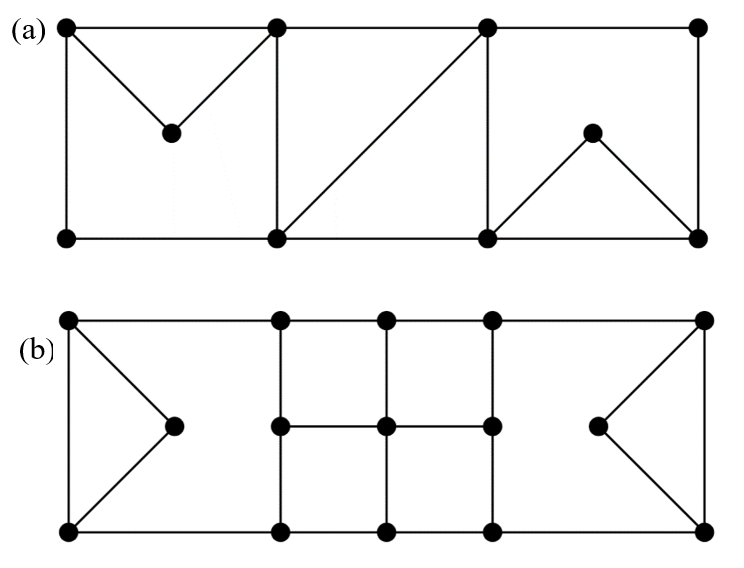
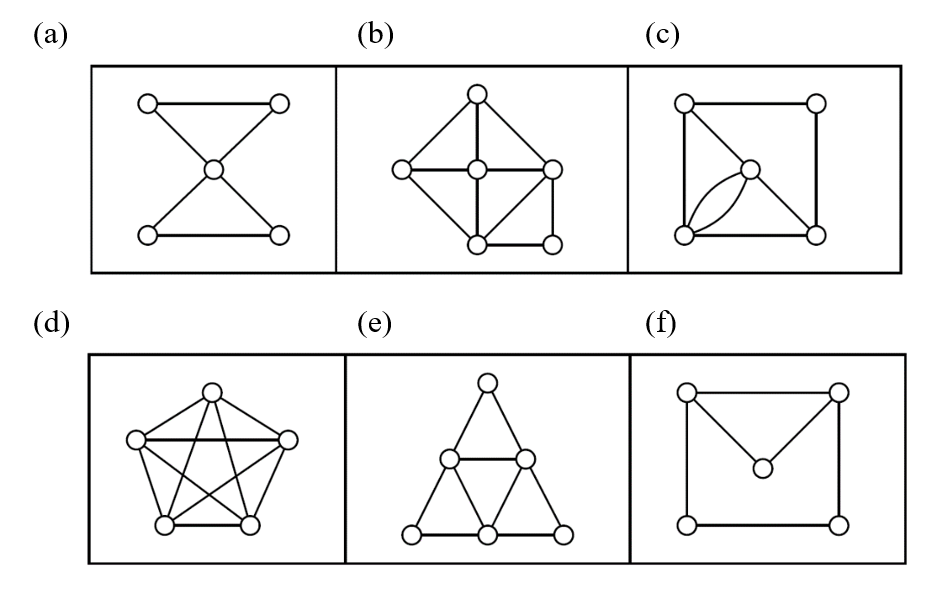
6. For each of the graphs in Figure 15.3.4 below, if one exists, find an Euler circuit or an Euler path. If an Euler circuit or path do not exists, explain why.
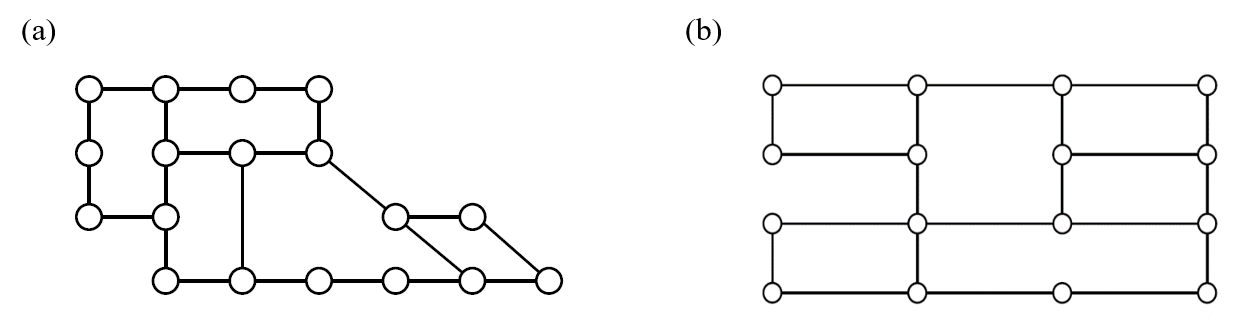
7. After a storm, the city crew inspects for trees or brush blocking the road. For the two neighborhoods shown in Figure 15.3.5 below, find an efficient route for the crew by finding an Euler circuit. If necessary, Eulerize the graph in an efficient way.
8. For the graphs in Figure 15.3.6, do each of the following: (i) identify whether the graph has an Euler circuit, an Euler path, or neither and explain why using theorems from this chapter; (ii) if the graph does have either an Euler path or circuit, find one; (iii) if the graph does not have an Euler path or circuit, Eulerize it so that it has an Euler circuit.